How Can I Perform Search and Track Using the Same Sensor?
- Jan 15, 2018
- Tech Tip
- Radar Systems
-
 Radar
Radar
In STK, the Radar object is used to perform Search and Track by making use of a Sensor object to point its Antenna. Analysis Workbench allows the sensor to switch modes by using two vectors in sequence.
- Create a Place object to host the Sensor and Radar. The primary sensor (in red) is used for analysis and to display the search and track modes. A secondary sensor that shows the Field of Regard (in blue) is used here for visualization only.
- Create a target (e.g., an aircraft object) that will be tracked by the Radar.
- Define the primary sensor pattern (e.g., Complex Conic).
- Define a geometric constraint on the primary sensor that can be used to determine the condition by which switching will occur.
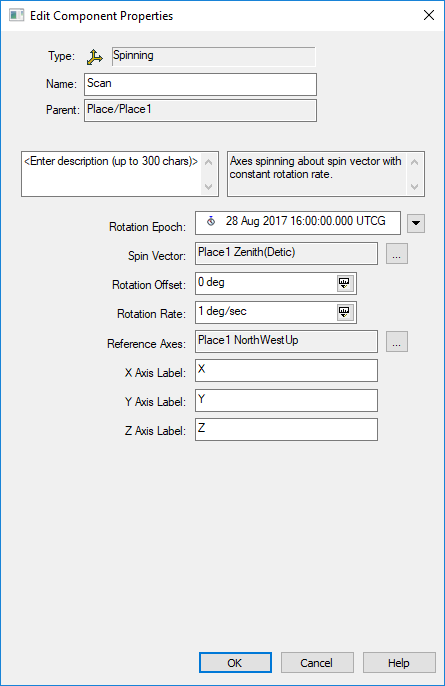
- Use the Vector Geometry Component of the Analysis Workbench to create a Custom Axes on the Place Object of type ‘Spinning,’ which will allow the Radar Antenna to scan when not tracking.
- Create an Access between the primary sensor and the target.
- Create a Vector of type ‘Scheduled,’ which will allow the sensor to switch modes.
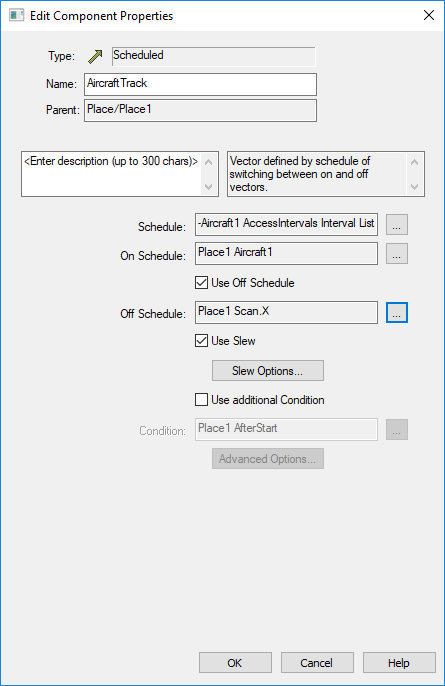
- Set the Schedule according to the Sensor to Target Access Interval List.
- Set On Schedule to use the Vector To the target during the Access.
- Set Off Schedule to use the X-axis of the Scan Axes previously created when there is no Access.
- Select ‘Use Slew’ if desired to slew between sensor modes.
- Click OK on Scheduled Vector properties.
- Select Pointing Type to be ‘Along Vector’ for primary sensor.
- Set Alignment Vector to be the Zenith(Centric) Vector for the Place object.
- Set the Constraint Vector to be the newly created Scheduled Vector.
- Create Antenna Object on primary sensor and create Radar Object on Place Object.
- Link Radar to Antenna.
- Perform Radar Analysis and generate reports and graphs as desired.
For more information on Radar, view our a six-part DIY series on Radar.

